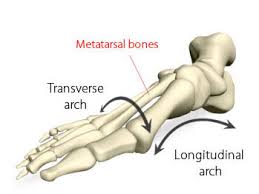
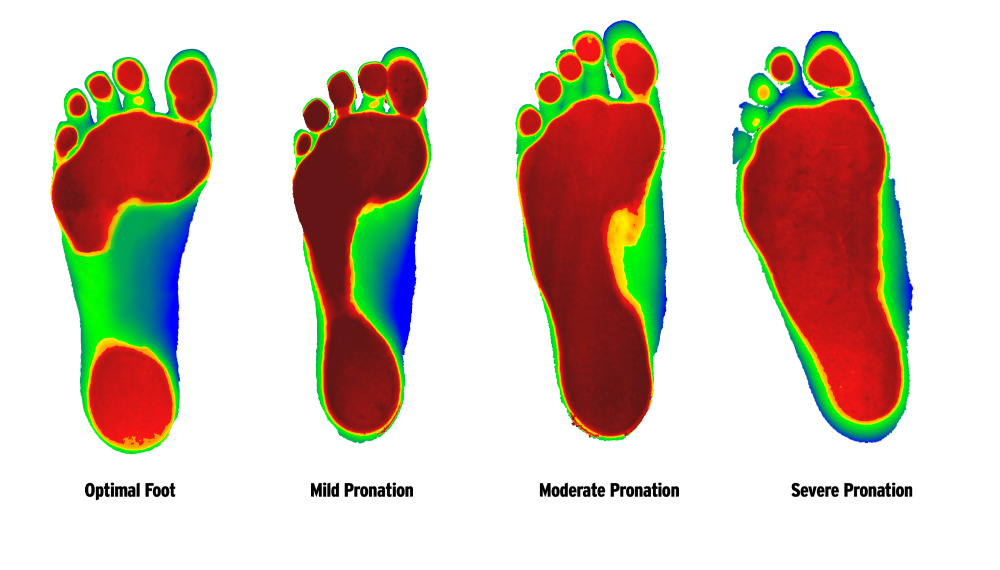
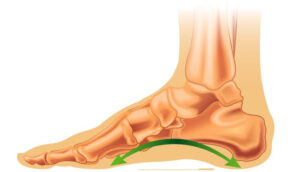
For people who fall under the “pronator” category, the arches of the feet fall down when walking – meaning that they have “flat feet” when standing.
Healthy medial arch (normal foot)
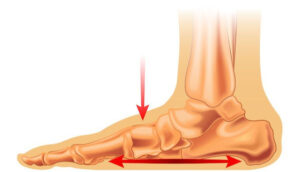
Collapse of the medial arch (flat foot)
For people who fall under the “supinator” category, this means that the arches of the feet are high and most of the weight is placed on the outer (lateral) edges of the feet.
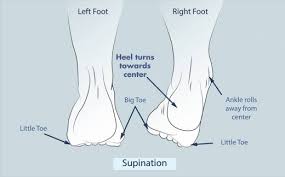
For people under the neutral category, this means that they have proper placement of their feet when walking or standing and the arches of the feet are placed correctly
Under the “pronator” and “supinator” category, the knee undergoes internal/external rotation to compensate for the low/high arches of the feet. This means that the ligaments, tendons and muscles associated with the movement and joints are strained in an incorrect way. There is extra pressure on the muscles and ligaments to pull the feet into correct alignment all the while maintaining your posture when standing and walking. This leads to incorrect mechanisms of the knee and hip joint as they work collectively to move your leg through the motions of walking. Due to the incorrect weight distributions throughout the joints problems like low back pain, knee pain and overall joint pain in the lower legs arise. When the joints are misaligned their ability to absorb impact when doing activities is reduced hence putting more force through the low back, knees and the ankles and feet causing joint pain and increased wear and tear in the joints.
Pronator

Supinator
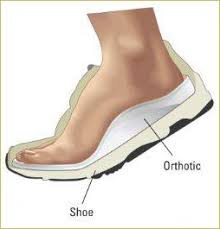
Once the orthotics are made, they are slipped into the appropriate footwear. Properly made orthotics help to re-align the position of your feet when walking. They help to lift the appropriate areas of the feet to provide extra support to the structures and ensure correct weight distribution.
What Conditions Do Orthotics Help With?
What are the symptoms? Pain at the joint when wearing ill fitting shoes. Redness, tenderness, warmth, and/or swelling where the joint bulges. Limited motion at the joint.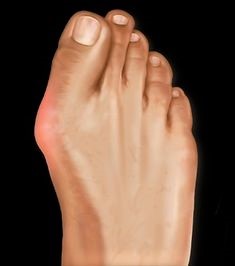
Causes of Bunions:
- Pressure on the big toe joint
- Improperly fitted shoes
- Flat feet, where the arch of the foot collapses to the ground when walking or standing
- Heredity/genetics
Treatment Protocols:
- Properly fitted shoes with a roomy toe, made of soft material (leather, suede)
- Stretching the joint to increase mobility
- Bunion shields and/or Bunions splits
- Physiotherapy: which may include electrotherapy, kinesio-taping, joint mobilization, foot posture correction program, and soft tissue massage all to decrease swelling and pain around the bunion, and increase mobilization of the foot
- Chiropractic care to optimize the joint biomechanics (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together) of the foot, knees, hips and pelvis to relieve joint stresses and inflammation. This will also help slow degenerative processes of abnormal wear and tear.
- Custom orthotics to support flat feet and unstable arches, to significantly relieve pain and pressure
Treatment Goals
- To alleviate tenderness, swelling and pain at the site and the tissue surrounding it
- To strengthen the arches of the foot
- To optimize the proper function of the foot
What are the symptoms? Knife like pain at the bottom of the foot, when first standing up in the morning. Intermittent or chronic pain that increases with running or jogging. Inflammation and/or swelling underneath the foot, or at the back the heel.
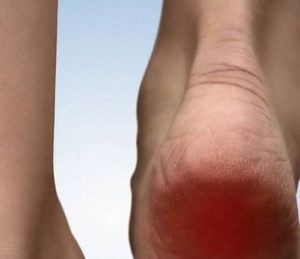
Causes of Heel Spurs
- Abnormal walking patterns that put pressure on the heel
- Running or jogging, especially on a hard surface
- Improperly fitted shoes
- Obesity
Treatment Protocols:
- Physiotherapy: which may include stretching and strengthening exercises for the foot muscles, laser over the heel, ultrasound, I.F.C. (electrical stimulation of the muscles,) night splints, shockwave therapy all to decrease pain and swelling, to relax and loosen the tissue around the heel spur and to increase mobility
- Properly fitted shoes
- Chiropractic care to restore the biomechanics of the foot, knees, hips and pelvis (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together)
- Custom orthotics to reduce the pain, stress and inflammation. Use of a heel spur gel cup as an option.
Treatment Goals
- To decrease the pain and swelling in the tissue around the heel spur
- To increase the mobility of the foot
- To restore the heel to its proper function
Knee pain is a very common complaint and can be acute or chronic. Pain can occur at the knee and the muscles around it, and it can radiate up or down the leg.
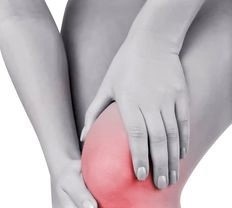
What are the symptoms? Limited movement. Inflammation, stiffness, and/or redness at and around the joint. Popping or crunching noises when moving the knee. Locking of the knee.
Causes of Knee Pain
- Wear and tear on the joint over time
- Arthritis
- Obesity
- Improper footwear
- Injury or trauma
- Muscle weakness
- Sports that involve running, jumping, pivoting
- Certain occupations that require repetitive strain on the knees
Treatment Protocols
- Stretching and strengthening the muscles
- Massage
- Physiotherapy: which may include I.F.C. and/or T.E.N.S/Laser treatments (electrical stimulation of the muscles and nerves) ultrasound, Proprioception (self-movement and body position) and balance exercises, Closed chain exercises (weight bearing), dry-needling and/or acupuncture all to reduce muscle pain, stiffness and swelling, and to strengthen the joint
- Chiropractic care to restore optimal biomechanics of the feet, knees, hips and pelvis to not only relieve pain, but also attempt to avoid the onset or progression of knee joint degeneration
- Custom orthotics to support leg and foot alignment
Treatment Goals
- To alleviate pain, stiffness and inflammation of the joint
- To reinforce the muscles supporting the knee
- To increase mobility of the joint
Lower back pain is experienced by over eighty percent of the population, at least once in their lifetime. The pain can affect the muscles, bones and nerves of the back.
 What are the symptoms? Pain involving the bottom five vertebrae of the spine (the lumbar region). Muscle spasms. Pain that radiates down the legs and can cause tingling or numbness. Pain that increases with prolonged sitting or standing. The pain can be acute, like a sharp stabbing or shooting sensation or chronic, like a dull ache that can last over three months.
What are the symptoms? Pain involving the bottom five vertebrae of the spine (the lumbar region). Muscle spasms. Pain that radiates down the legs and can cause tingling or numbness. Pain that increases with prolonged sitting or standing. The pain can be acute, like a sharp stabbing or shooting sensation or chronic, like a dull ache that can last over three months.
Causes of Low Back Pain
- Weakness in the back and abdomen muscles
- Poor posture
- Injury or trauma
- Sciatica or muscle strain
- Bulging disks or degenerative disk disease
- Jobs that require heavy lifting or prolonged sitting
- Arthritis
Treatment Protocols
- Physiotherapy: which may include stretching and strengthening the back and abdominal muscles, soft tissue manual therapy, laser treatment, F.C. (electrical stimulation of the muscles), kinesio-taping, or ultrasound all to relieve pressure, swelling, chronic pain and tenderness and increase circulation, in the low back.
- Massage therapy to relax the muscles and relieve pressure
- Chiropractic care to restore normal spine and pelvis function and to relieve nerve pressure and irritation, that not only causes low back pain, but also compromises one’s health and well being
- Posture correction and ergonomic education
- Custom orthotics to stabilize the feet, knees and pelvis which helps relieve abnormal stress and strain on the lower back
Treatment Goals:
- To reduce chronic pain, pressure, muscle spasms and swelling
- To stabilize the lower back, pelvis, knees and abdominal muscles
- To recondition the lower back to its normal function
Achilles tendonitis affects the tough connective tissue band (tendon) that joins the calf muscle to the heel bone. It is common in runners, tennis, and basketball players. Increased activity can lead to a tear in the tendon.
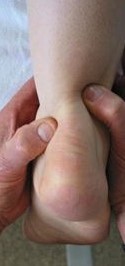
What are the symptoms? Pain, stiffness, warmth, and/or inflammation in the tendon and the back of the heel. Soreness and dull ache in the calves of the legs. Pain increases with prolonged physical activity. Range of motion is limited when flexing the foot.
Causes of Achilles Tendonitis or Pain:
- Improper warmups before exercise or a sudden increase in physical activity
- Calf muscle strain
- Incorrect athletic footwear or high heels
- Heel/bone spurs
- Repetitive strain on the Achilles tendon
Treatment Protocols:
- Ice to reduce the inflammation
- Rest to decrease the pain in the tendon and calf muscles
- Physiotherapy: which may include stretching and strengthening exercises, soft tissue massage, kenisio-taping, ultrasound, and heat therapy all to reduce pain in the tendon, tightness in the calves and increase range of motion
- Chiropractic care to restore the biomechanics of the foot and leg (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together)
- Custom orthotics to promote healing and relieve stress on the Achilles tendon and reduce strain on the calf muscles.
Treatment Goals:
- To reduce pain and inflammation in the tendon, heel and calf muscles
- To strengthen and increase the flexibility of the calf muscles and the Achilles tendon
- To adopt proper exercise routines and prevent future injury to the tendon
- To take active support measures to prevent further occurrences
Ball of foot pain is also known as Metatarsalgia or Morton’s or Intermetatarsal Neuroma, and usually occurs between the third and fourth toes but can affect any toes on the foot. Pain in the ball of the foot makes it difficult to stand on or walk. It is often compared to walking on a pebble or marble stuck in one’s shoe.
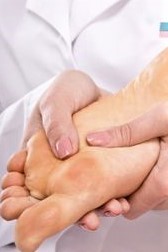
What are the symptoms? Gradual aching in the ball of the foot, that becomes sharper and more intense overtime. Burning sensation in the ball of the foot. Tingling or numbness from compression of the nerves in the toes. Pain that worsens when walking or running.
Causes of Ball of Foot Pain:
- Improper footwear, such as high heels
- Foot deformities and conditions such as fallen or high arches, bunions, calluses, hammer toe, or gout
- Pressure or injury to the nerves in the toes
- Sesamoiditis: inflammation or injury to the sesamoid bones (two pea shaped bones in the ball of the foot beneath the big toe)
- Osteoarthritis
- Obesity
Treatment Protocols:
- Ice to reduce the pain and inflammation,
- Rest and elevate the foot
- Proper footwear
- Metatarsal and/or callus pads to cushion to swollen area
- Physiotherapy which may include stretching exercises to loosen the tendons and ligament of the affect toes, strengthening exercises for the ankle, laser, electrotherapy, soft tissue massage, kinesio-taping and acupuncture all aim to decrease pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot and the nerves of the affected toes
- Chiropractic care to correct the biomechanics and function of the ankle, foot, knee and pelvis to relieve stress and pain and ensure that the body weight is evenly distributed across the feet, in order to alleviate the stress and thus, the pain in the ball of the foot
- Custom orthotics to support and align the arch of the foot in order to take pressure off the ball of the foot
Treatment Goals:
- To lessen the pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot
- To release pressure on the nerves in the affected toes
- To restore proper gait biomechanics and provide adequate support for long term correction of the foot and lower leg kinetic chain (how the lower body works to promote or inhibit movement)
Plantar Fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain and occurs when the tendon at the bottom of the foot, that supports the arch, becomes inflamed.
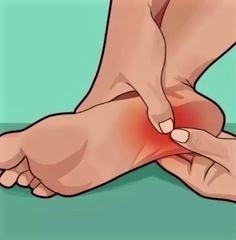
What are the symptoms? The inflammation causes pain, stiffness and tenderness at the heel and the bottom of the foot. The pain is most severe in the morning after the first few steps. Pain can also increase after walking and exercise.
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
- Repetitive stress and strain from activities like running, on the tendon/fascia
- Improper footwear
- Improper gait
- Flat feet or high arches that irritate the tendon
- Occupations that require long hours of standing
- Obesity
Treatment Protocols:
- Ice to reduce the swelling and pain
- Exercise to strengthen muscles of the foot
- Stretching the calf muscle
- Physiotherapy: which may include ultrasound treatment, kinesio- taping, shockwave therapy, manual therapy, and T.E.N.S, (electrical stimulation of the nerves) to reduce the inflammation of the tendon
- Chiropractic care to reduce the pain and restore the biomechanics (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together) of the foot, knee and pelvis. Trigger point therapy to relieve muscle and tendon pain, and spasm.
- Custom orthotics to lessen the pain and restore the function of the foot and heel
Treatment Goals:
- To reduce pain and inflammation in the heel
- To improve the function of the damaged tendon
- To restore the biomechanics of the foot (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together)
A sprained ankle is a very common injury. It occurs when you twist or turn your ankle in an awkward way so that the ligaments get stretched and can possibly tear.
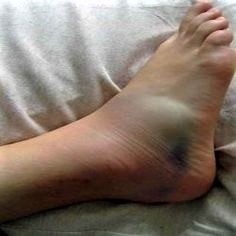
What are the symptoms? Swelling, bruising, tenderness and/or pain in the tissue surrounding the ankle. Pain and instability when standing and bearing weight on the affected foot. A limited range of motion and stiffness around the ankle.
Causes of a sprained ankle
- Exercises like running, or walking on an uneven surface
- Tripping or falling in a way that twists the ankle
- Unsupportive footwear
- Certain sports that involve running, jumping and pivoting
- Recurrence of the sprain is possible if the original sprain was not treated properly
Treatment Protocols:
- Rest, ice and elevate the ankle
- Apply a compression bandage around the ankle to contain the swelling
- Physiotherapy: which may include ultrasound, laser, range of motion exercises for the ankle, foot strengthening exercises, I.F.C and T.E.N.S (electrical stimulation of the muscles and nerves) proprioception (self- movement and body position) and balance exercises, all to decrease swelling and pain and increase stability and mobility of the ankle and foot
- An ankle brace or boot to stabilize and immobilize the ankle as it heals
- Chiropractic care to reduce the pain and restore the biomechanics of the foot and knee (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together)
- Custom orthotics stabilize the joint, advance the healing process and prevent further injury
Treatment Goals:
- To reduce swelling and pain around the ankle
- To accelerate the course of healing of the sprain
- To stabilize the joint and allow for better mobility
- To prevent future sprains from occurring
Arch pain occurs when the arch of the foot is unable to bear weight or absorb the shock of surface contact when standing, walking or running.
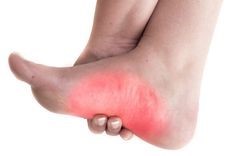
What are the symptoms? Pain, tenderness and redness in the arches, pain in the heel and ball of the foot. Pain in the joints of knee, ankle and/or hips can also occur. Pain usually increases when standing, walking or other activities. Inability to bear weight on the foot.
Causes of Arch Pain:
- Low arches (overpronation) or high arches (cavus foot) can affect the biomechanics (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together) of the foot
- Sprains, strains, stress fractures or other trauma that affects the foot
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Heredity/Genetics
- Improperly fitted footwear
Treatment Protocols:
- Rest, avoidance of strenuous physical activity
- Proper footwear that supports the arch
- Ice to reduce swelling and alleviate pain
- Physiotherapy: which may include stretching exercises, night splints, braces, ultrasound, andF.C. and/or T.E.N.S (electrical stimulation of the muscles and nerves) all which will reduce pain, increase circulation and mobility
- Chiropractic care to reduce the pain and restore the biomechanics (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together) of the foot, knee and pelvis. Trigger point therapy to relieve muscle and tendon pain, and spasm.
- Custom orthotics to provide proper arch support and stabilize the foot
Treatment Goals:
- To reduce pain and inflammation
- To increase mobility and stability in the arches
- To restore proper function to the biomechanics of the foot and the affected toe joints (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together
Claw toes bend at the middle and end joints of the toe, causing the toes to have a claw or talon like appearance and usually affect the last four digits of the foot.
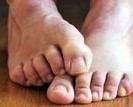
What are symptoms? Pressure and pain, where the buckled toes rub against the footwear. Corns and calluses from the toes chafing against the top of the footwear. Ulcers may develop on the toes in diabetic patients
Causes of claw toes or claw foot:
- Improperly fitted shoes (tight shoes, high heels)
- High arches
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid or osteo-arthritis
- Heredity/Genetics
Treatment protocols:
- Proper footwear with toe room and arch support
- Ice to reduce swelling
- Pads for corns and calluses
- Physiotherapy: which may include kinesio-taping, stretching exercises, ultrasound, andF.C (electrical stimulation of the nerves) all to reduce pain, swelling, and promote joint stability
- Chiropractic care to restore the biomechanics (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together) of the foot, knee and pelvis as well as the affected toe joint.
- Custom orthotics to stabilize the affected toes and provide proper arch support
Treatment Goals:
- To decease pain and swelling in the effected toe joints
- To strengthen and stabilize the toe joints
- To increase joint mobility and foot function
Stress fractures are tiny cracks that often occur in the bones of the lower leg and feet. Anyone can develop a stress fracture in any bone – but runners, track and field athletes, or anyone who participates in exercises that bear excessive weight on the lower extremities, are prone to stress fractures in the legs and feet.
What are the symptoms? Tenderness, swelling and possible bruising that starts in and around the crack in bone. Fractures usually occur in the shin bone (tibia), the ankle, the toe bones (metatarsals,) heel bone (calcaneus),and the navicular bone, (at top inner side of the foot). Pain intensifies with increased activity.
Causes of Stress Fractures:
- Repetitive force or weight placed upon the bone over time
- Improper bone and/or muscle alignment
- Osteoporosis (low bone mass/deterioration of the bone tissue)
- High arches (Pes Cavus) or Flat feet (Pes Planus)
- Worn or improper footwear
Treatment Protocols:
- Ice to reduce swelling
- Rest and elevate the affected area to alleviate pain
- Physiotherapy: which may include, kinesio-taping, soft tissue massage, brace/boot, ultrasound, andF.C. and T.E.N.S (electrical stimulation of the muscles and nerves), controlled weight bearing exercises, all of which will decrease pain and inflammation, and stabilize and strengthen the area affected by the fracture
- Chiropractic care to reduce pain and restore the biomechanics of the leg or foot (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together)
- Custom orthotics to provide stability and promote proper weight bearing of the affected leg or foot
Treatment Goals:
- To promote healing and bone fusion of the stress fracture
- To reduce swelling and pain
- To improve and reinforce the stability of the affected leg or foot
Iliotibial band syndrome is an injury or pain to the connective tissue (iliotibial band) that runs from the hip along the outside of the thigh down to the top of the lower knee bone (tibia). It often occurs in exercises where the knee repetitively bends with high intensity activity exercises like running, cycling, or hiking.

What are the symptoms? Tenderness, burning, aching and/or pain along the thigh and outside of the knee. Inflammation and irritation of the actual band/connective tissue. Warmth, redness and/or stinging, sensation on the outside of the knee. Clicking or popping sounds on the outside of the knee.
Causes of Iliotibial Band Syndrome:
- Weakness in the hip abductor muscles (which help rotate and side lift the leg at the hip joint)
- Pelvic tilt causing weakness and/or tightness in the thigh muscles
- Activities like cycling, rowing, hiking, running up and down stairs
- Long distance running on uneven surfaces which cause the foot to roll
- Improper exercise warmup or cool down
- Difference in leg lengths
Treatment Protocols:
- Rest and ice the knee and outside of the thigh
- Massage
- Physiotherapy which may include stretching and flexing exercises, strengthening the hip muscles, ultrasound, and I.F.C. and/or T.E.N.S (electrical stimulation of the muscles and nerves), and kinesio-taping. All of which will reduce pain and inflammation to the outer knee, and decrease stress and tightness on the iliotibial band
- Chiropractic care to adjust and correct the biomechanics of the hips, pelvis and spine, exercises and trigger therapy to strengthen the hip abductor muscles, and take pressure and strain off the iliotibial band, ensuring that the body weight is evenly distributed across the feet and knees in order to alleviate the stress and pain in the hip
- Custom orthotics to assist with leg length discrepancy, accommodate a pelvic tilt, and prevent the foot from rolling on uneven surfaces
Treatment Goals:
- To alleviate pain and swelling along the iliotibial band and the outer side of the knee
- To reinforce weak hip abductor muscles
- Restore proper gait mechanics and provide proper support measures for long term correction and alleviation of abnormal stresses being placed on the hip, pelvis and knee
A Hammer toe occurs when the middle joint of the toe bends abnormally and curls inward.
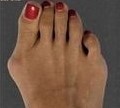
What are the symptoms? Mild to severe pain, redness and/or swelling in the affected toe. Restricted movement. Discomfort when walking. Corns and calluses.
Causes of Hammer Toe:
- An imbalance or weakness in the muscles, tendons or ligaments that cause the toe to bend into a hammer shape
- Toe length, if the second toe extends beyond the big toe, it is more at risk of developing Hammer Toe
- Injuries such as a broken or stubbed toe
- Improperly fitted footwear such as tight shoes, high heels
- Arthritis or diabetes
- Heredity/Genetics
Treatment Protocols:
- Shoes with a roomy box and low heels
- Corn pads
- Ice to reduce swelling
- Physiotherapy: which can include toe stretches and exercises, kinesio-taping, toe brace, ultrasound, andF.C. and/or T.E.N.S (electrical stimulation of the muscles and nerves) all to decrease pain and swelling in the toe, and promote joint stability
- Chiropractic care to reduce the pain and restore the biomechanics of the foot and the affected toe joint (restore how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together)
- Custom orthotics to stabilize the toe joint and promote healing
Treatment Goals:
- To reduce pain and swelling in the affected joint
- To stabilize the joint
- To increase toe joint mobility and function
Flat feet also known as Pes Planus, or Fallen Arches occurs when the arch of the foot collapses as it contacts a surface, bearing weight on the foot unevenly (overpronation). Up to 25 % of the population can have one or both arches that do not develop properly.
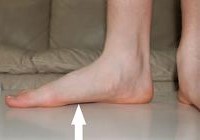
What are the symptoms? Pain in the heel, ankle, or inside of the collapsed arch. Aching and pain in the shins, hips, knees and/or lower back. Inflammation along the inside of the ankle. Foot “fatigue” or tiredness. Restricted foot movement, such as the inability to stand on one’s toes.
Causes of Flat Feet:
- Improper arch development in childhood/genetics/heredity
- Foot or ankle injury or trauma
- Inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon (that connects the lower leg, along the ankle to the foot’s arch)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Leg-length inequality
Treatment Protocols:
- Massage
- Physiotherapy: which may include stretching and strengthening exercises and foot gymnastics, ankle braces or shoe wedges, ultrasound, all to reduce inflammation, increase mobility and to treat referred pain
- Chiropractic care to reduce the pain and restore the biomechanics (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together) of the foot, knee and pelvis. Trigger point therapy to relieve muscle and tendon pain and spasm.
- Custom orthotics to relieve pressure and prevent the foot from rolling inward
Treatment Goals:
- To alleviate pain caused by unequal distribution of weight
- To strengthen to foot and the joints affected by fallen arches
- To realign the body with orthotic inserts and restore proper posture
A Mallet toe occurs when the joint closest to the toenail bends abnormally and usually affects the second, third and fourth toe.
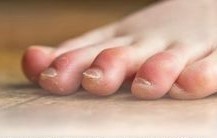
What are the symptoms? Mild to severe pain and swelling in the affected toe. Restricted movement. Discomfort when walking. Corns and calluses.
Causes of Mallet Toe:
- An imbalance or weakness in the muscles, tendons or ligaments that cause the toe curve downward at the first joint
- Injuries or trauma to the toe
- Improperly fitted footwear such as tight shoes that cram the toes together
- Arthritis or diabetes
- Heredity/Genetics
Treatment Protocols:
- Shoes with a roomy box and low heels
- Corn pads
- Ice to reduce swelling
- Physiotherapy: which may include toe stretches and exercises, kinesio-taping, toe braces, all to decrease pain and swelling in the toe, and promote joint stability
- Chiropractic care to reduce the pain and restore the biomechanics of the foot and the affected toe joint (restore how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together)
- Custom orthotics to stabilize the toe joint and promote healing
Treatment Goals
- To reduce pain and swelling in the affected joint
- To stabilize the joint
- To increase toe joint mobility and function
High arches, also known as Pes Cavus occur when the foot rolls outward as it steps down, placing force on the outer part of the foot, as the arches are too hollow to bear down the full weight of the step.
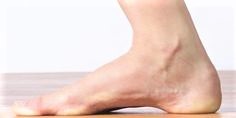
What are the symptoms? Pain when standing or walking. Ankle instability, which can lead to tripping/falling and cause sprained ankles. Calluses on the ankle, ball or sole of the foot. Knee, hip and back pain. High arches can cause other foot problems such as hammer toe, claw foot, or plantar fasciitis.
Causes of High Arches:
- Genetics/heredity
- Neurological disorders such as Charcot Marie Tooth disease, polio, spina bifida, stroke, spinal tumour, muscular atrophy, cerebral palsy, or clubfoot all of which can cause muscle imbalance in the lower leg and draw the arch upward and the heel downward
Treatment Protocols:
- Ice to reduce the inflammation and pain
- Physiotherapy: which may include stretching and strengthening exercises,foot pads, ankle braces and/or night splints all to improve muscle tone, tendon mobility and ankle stability
- Chiropractic care adjustments to align the back, hips, knees and feet to provide pain relief and balance to the lower leg
- Custom orthotics to redistribute weight and pressure evenly and provide stability for the ankle
Treatment Goals:
- To provide ankle strength and mobility
- To reduce pain and inflammation
- To prevent other foot conditions like hammer toe, claw foot or plantar fasciitis from occurring
Shin Splint syndrome is also called Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome and often occurs in runners, dancers and those in the military. It can develop when added stress is placed on the shin bone (tibia), the bone that connects the knee to the ankle bone.
What are the symptoms? Inflammation and pain in the lower leg. Throbbing or aching of the shin bone and the muscles attached to it. The pain and tenderness can increase with exercise, like running or dancing,or other high impact activities, that put pressure on the shin bone. The pain decreases with rest.
Causes of Shin Splint Syndrome
- Flat feet, where the foot’s arch collapses when walking, running
- High arches that cause instability of the foot
- Improperly fitted footwear
- Muscle weakness in ankles and hips and core muscles
- Improper training techniques
General Treatment Guidelines
- Rest and ice the shin bone
- Physiotherapy: which may include stretching and strengthening, Kinesio-taping, correcting gait pattern and recommending appropriate footwear, manual therapy, activity modification – all of which will loosen tight muscles, strengthen weak muscles, reduce pain and swelling and maintain stability
- Chiropractic care to decrease pain, restore and stabilize the knee, ankle and foot joints.
- Custom orthotics to provide support for the arch of the foot in order to take the stress off the tibia (shin)
Treatment Goals
- To reduce pain and inflammation in the lower leg
- To maintain stability and strengthen the core, hip and lower leg muscles
- To supply support for the arch and reduce pressure on the tibia
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome is sometimes known as “Runner’s Knee” or “Jumper’s Knee” because it can occur in people involved in extended periods of running, jumping, squatting and athletic training.

What are the symptoms? Dull, throbbing pain at the front of the knee and around the kneecap (patella). The patellofemoral joint is located just over the kneecap and below the femur (the long bone of the thigh).
Causes of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
- Vigorous activity and sports that include running, jumping or climbing that put extra pressure on the knee
- Muscle imbalance around the hip or knee that lead to misalignment of the knee
- Fracture or dislocation of the kneecap
- Improper use of sports equipment or unhealthy training techniques
Treatment Protocols
- Rest, ice and elevate the knee
- Compression: wrap a tensor bandage around the knee, leaving the kneecap area open
- Physiotherapy: which may include exercises to strengthen the muscles that support the knee, kinesio-taping, manual therapy, proprioception training (self-movement and body position) all to reduce pain at and around the kneecap and strengthen the muscles that support the knee
- Chiropractic care to realign the spine, hip, knee and ankle to restore balance and alleviate the pressure on the patellofemoral joint
- Custom orthotics to stabilize and support proper foot, knee, hip and pelvis joint biomechanics (how the muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments work together)
Treatment Goals
- To alleviate the pain the at kneecap (patella), and surrounding muscles
- To build up the muscles around the kneecap, taking pressure off the patellofemoral joint